‘DSL’
stands for ‘digital subscriber line’. The term is a general term applied to a
variety of different technologies used to achieve ‘broadband’ or high speed
digital transmission over 2-wire or 4-wire ‘standard copper’ public telephone network
access lines – usually for the purpose of high speed Internet connection. All
DSL technology can be subdivided into one of two types:
4 SDSL
(symmetric digital subscriber line) and
4 ADSL
(asymmetric digital subsriber line)
The prime
difference between ‘SDSL’ and ‘ADSL’ is the speed of transmission in the ‘downstream’ direction (the direction
from the network towards the user) – relative to the speed of transmission in
the ‘upstream’ direction (te
direction from the user towards the network). In SDSL the transmission rate in downstream and upstream directions is the same (i.e. symmetric). In ADSL, the downstream
rate of transmission is greater than the upstream
bitrate (i.e. asymmetric). The
commonest form of DSL is ADSL.
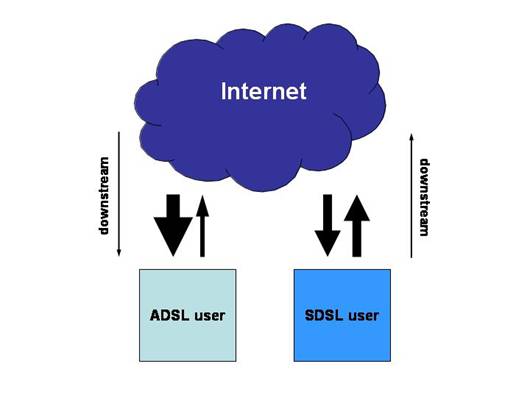
upstream
and downstream flows: the difference between ADSL and SDSL
Other types of DSL
As well as
SDSL and ADSL, a number of other DSL abbreviations and ‘types of DSL’ have been
invented over time. These include: HDSL, XDSL, VDSL. In reality, these are all
variants of the basic SDSL and ADSL types of DSL or simply alternative
terminology:
4 HDSL (high
speed digital subscriber line) is a particular type of SDSL – usually providing
2 Mbit/s transmission in both downstream and upstream directions
4 VDSL (very high
speed digital subscriber line) is able to operate at very high speed (e.g. up
to 50 Mbit/s) over copper cable – but only over short distances. Typically VDSL
is used in ‘hybrid’ networks, comprising short copper cable connections from
VDSL customer premises to locally placed street cabinets and then by means of
glass fibre to the network operator’s exchange building site (this type of
hybrid network is sometimes referred to as ‘fibre-to-the-curb’ (FTTC)).
4 XDSL is
sometimes used as a generic term to mean ‘any type of DSL’. The ‘X’ stands in
place of a letter making up a recognised DSL abbreviation. Thus XDSL may be
used as a shortform to mean ‘any of: ADSL, HDSL, SDSL, VDSL etc.)